Polyline map
Written by
Updated at March 6, 2025
A polyline map is a type of geolayer on a Map chart that lets you draw polylines on the map. A polyline consists of points connected in a certain order. A polyline map is used, for example, to show the path of a moving object.
To build a polyline map, you need the following data:
- Coordinates of line points of the Geopoint data type. Each point of each polyline must be stored in a dataset as a separate row.
- A field or a set of fields to group points into lines (each line's ID).
- A field to sort the order of points in each line (such as a timestamp or point number).
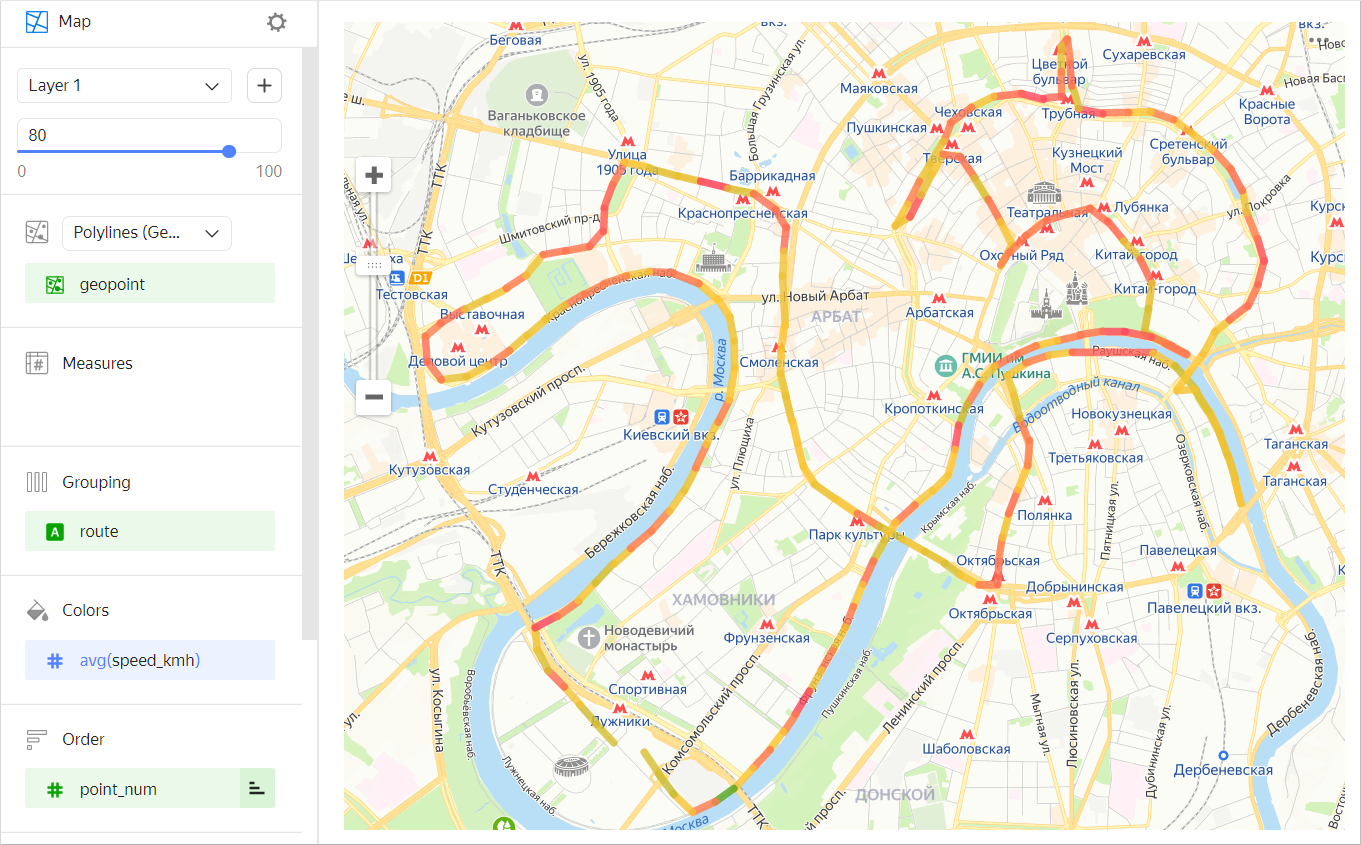
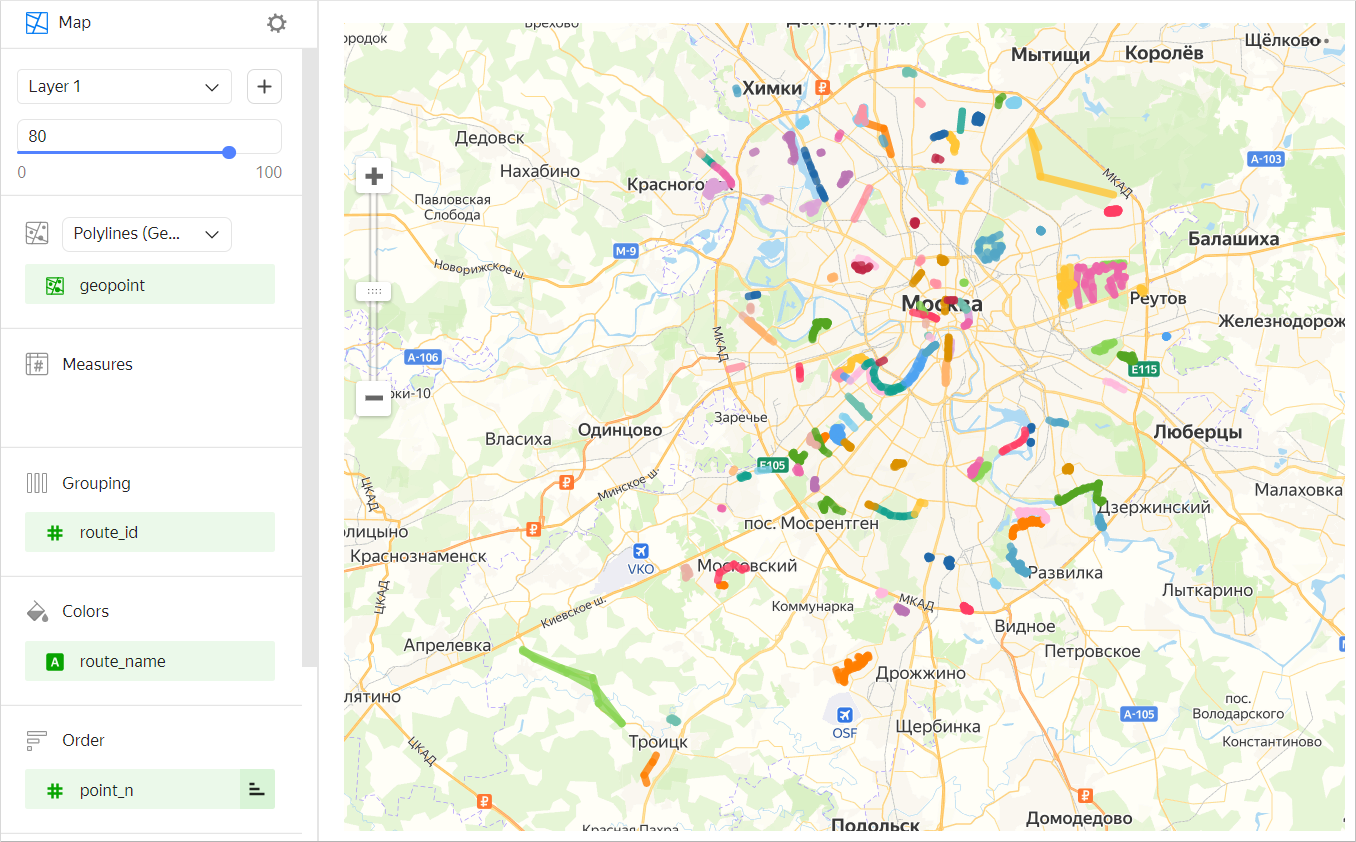
You can color polyline segments in one of the following ways:
-
In a gradient by measure (for a example, an average speed in a point).
-
In discrete colors by dimension (for example, by trip name).
Wizard sections
| Wizard section |
Description |
|---|---|
| Polylines (Geopoints) | Measure of the Geopoint type |
| Measures | Measure. The value displayed when you hover over a point. |
| Grouping | Dimension. Defines a group of points forming a polyline. |
| Colors | Dimension or measure. Affects the intensity of line segment fill. A segment is filled in from the originating point. |
| Order | Dimension. Defines the order for connecting points within a group. |
| Layer filters | Dimension or measure. Used as a filter for the current layer. |
| Filters | Dimension or measure. Used as a filter for the entire chart. |
Creating a polyline map
To create a polyline map:
Warning
If you use a new DataLens object model with workbooks and collections:
- Go to the DataLens home page
- Open the workbook, click Create in the top-right corner, and select the appropriate object.
Follow the guide from step 4.
- Go to the DataLens home page
- In the left-hand panel, select
- Click Create chart → Chart.
- At the top left, click
- Select Map for chart type.
- Select the Polylines (Geopoints) layer type.
- Drag a dimension of the Geopoint type from the dataset to the layer type selection section.
- Specify a group of points that defines polylines. Move the measure to the Grouping section.
- Define the order for connecting points within the group. Move the measure to the Order section.
- Color the line on the map. Move the measure or dimension to the Colors section.
You can also:
- Add, rename, and delete a layer.
- Apply a filter to the whole chart or one layer.
Recommendations
- Reduce the number of route points at the source level if there are too many of them. To do this, use a chart-level filter. This will speed up map loading and rendering.
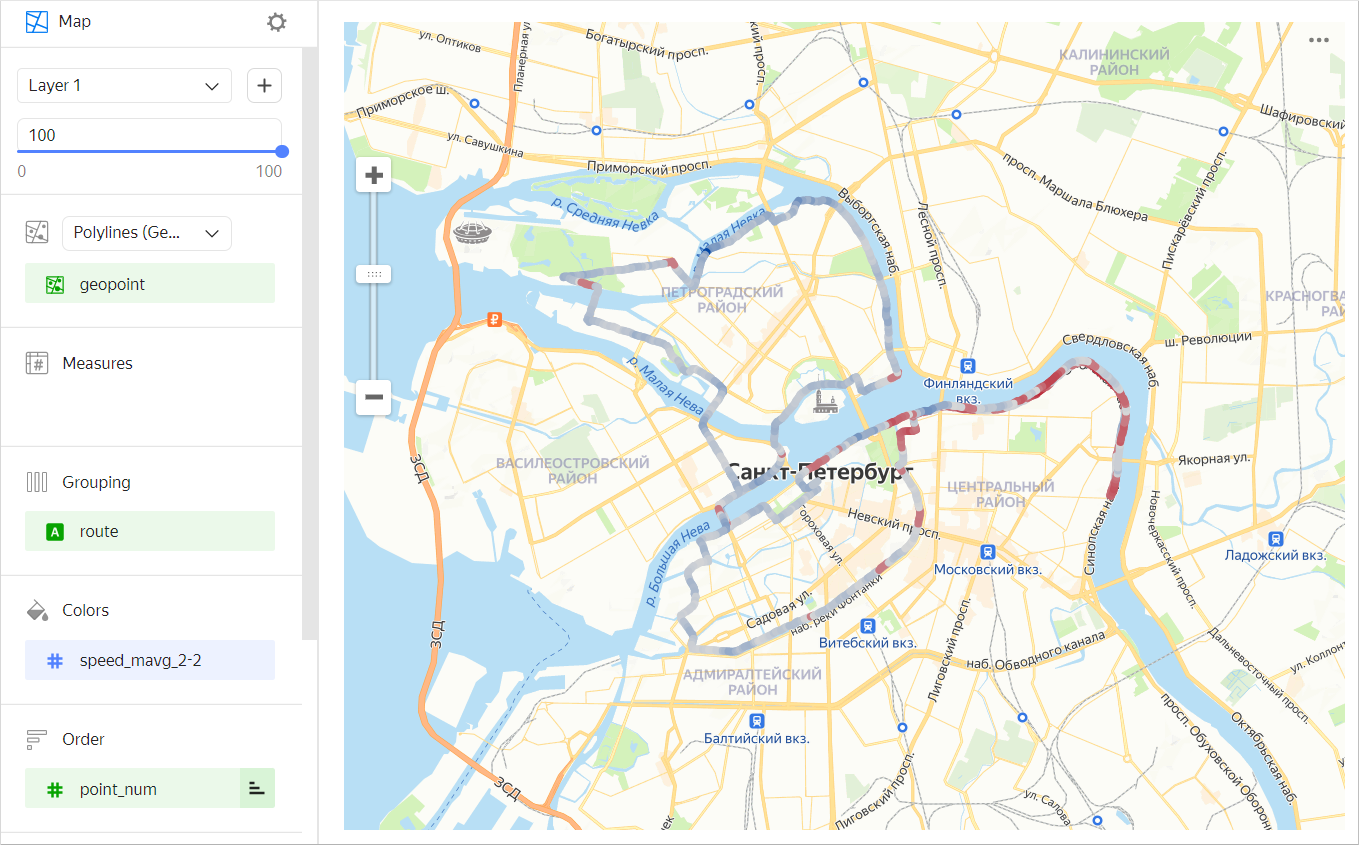
- Use the MAVG moving average function to smooth measure outliers of individual points/sections. For example, when building a line representing average speed using the
MAVG([speed],2,2)function, the speed measure values are averaged out in the current point, as well as two points before and two points after it. As a result, the color gradient changes more smoothly.