How access management works in Yandex Cloud
Here you can learn how to manage access to your resources and how IAM checks permissions to access them.
How are access permissions verified?
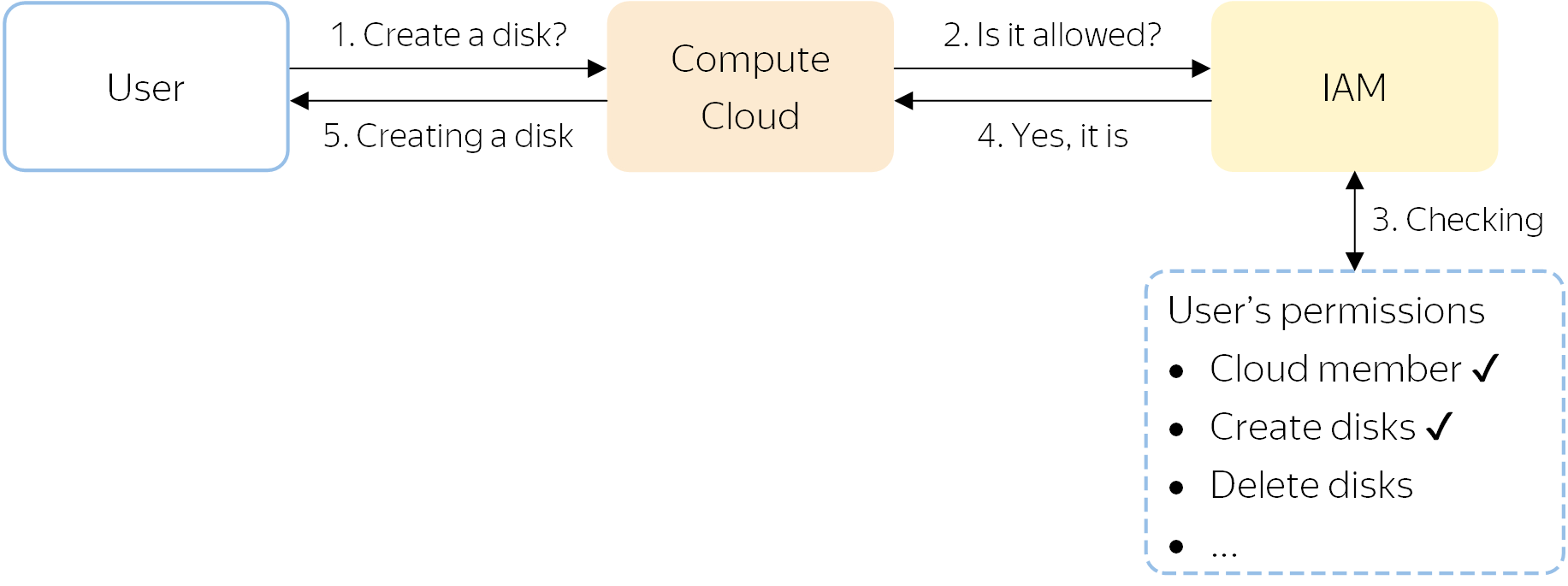
All operations in Yandex Cloud are first sent for verification to IAM. For example:
- A user requests Compute Cloud to create a new disk in the
default
folder. - Compute Cloud sends a request to IAM to check whether this user is allowed to create disks in this folder.
- IAM checks if the user is a member of the cloud with the
default
folder and has the necessary permissions to create a disk in this folder. - If any of the permissions are missing, the operation is not allowed and Yandex Cloud returns an error.
If all the required permissions were granted, IAM reports this to the service. - The service creates a new disk.
How do I perform access management?
Access management in Yandex Cloud leverages the Role Based Access Control
To assign a role, you need to select a resource, choose a role, and describe the subject getting the role. As a result, the subject gets permissions to access the resource.
You can also assign a role for a parent resource to inherit access permissions from, e.g., a folder or cloud.
Warning
It usually takes 5 seconds or less to update access permissions. If the role was assigned to you, but you do not have access yet, repeat the operation.
For example, you were given the right to create folders in the cloud and you were able to create one folder, but couldn't create another one. This is because the access permissions have not yet been updated on the server where the second create folder operation was performed. Try creating the folder again.
Resources you can assign roles for
You can assign roles for a cloud, folder, and other resources from the list. If you need to grant access to a resource that is not on the list, assign the role for the parent resource it inherits permissions from. For example, Yandex Managed Service for PostgreSQL clusters inherit access permissions from their folder.
Role
To assign roles for a resource, you need to have one of the following roles for that resource:
adminresource-manager.adminorganization-manager.adminresource-manager.clouds.ownerorganization-manager.organizations.owner
Thus, roles for a resource can be assigned by users with the administrator role for the cloud or organization, as well as by the owners of the cloud or organization to which the resource belongs.
Each role consists of a set of permissions that describe operations that can be performed with the resource. A user can assign a role with only those permissions which are available to themselves. For example, only the user with the cloud owner role can assign this same role. The administrator role is not enough for this.
For information about available roles and permissions they offer, see Roles.
Subjects that roles are assigned to
Roles are assigned to subjects. There are the following subject types:
-
userAccount: Yandex account added to Yandex Cloud or an account from a user pool:Subject ID:
userAccount:<user_ID>.Where
<user_ID>is the unique ID assigned to the user, e.g.,userAccount:ajecpdmpr4pr********. -
serviceAccount: Service account created in Yandex Cloud:Subject ID:
serviceAccount:<service_account_ID>.Where
<service_account_ID>is the unique ID assigned to the service account, e.g.,serviceAccount:ajevnu4u2q3m********.You can assign roles to a service account for any resources in any cloud if these resources belong to the same organization as the service account. You can also assign roles to a service account for the organization.
-
federatedUser: User account in an identity federation, e.g., Active Directory.Subject ID:
federatedUser:<user_ID>.Where
<user_ID>is the unique ID assigned to the federated user, e.g.,federatedUser:aje7b4u65nb6********. -
group: Yandex Identity Hub user group:-
User group created by the organization administrator:
Subject ID:
group:<user_group_ID>.Where
<user_group_ID>is the unique ID assigned to the user group created by the organization administrator, e.g.,group:ajeser8mnc4c********. -
All users in organization Xsystem group:Subject ID:
group:organization:<organization_ID>:users.Where
<organization_ID>is the unique ID assigned to theXorganization, e.g.,group:organization:bpfaidqca8vd********:users. -
All users in federation Nsystem group:Subject ID:
group:federation:<federation_ID>:users.Where
<federation_ID>is the unique ID assigned to theNidentity federation, e.g.,group:federation:bpf8tpgggfoi********:users.
-
-
system: Public group of users:-
All authenticated userspublic group of users:Subject ID:
system:allAuthenticatedUsers. -
All userspublic group:Subject ID:
system:allUsers.
-
Assigning access permissions
Roles for a resource are assigned as a list of role-subject bindings. They are called access bindings. You can add or remove these bindings to control permissions to access a resource.
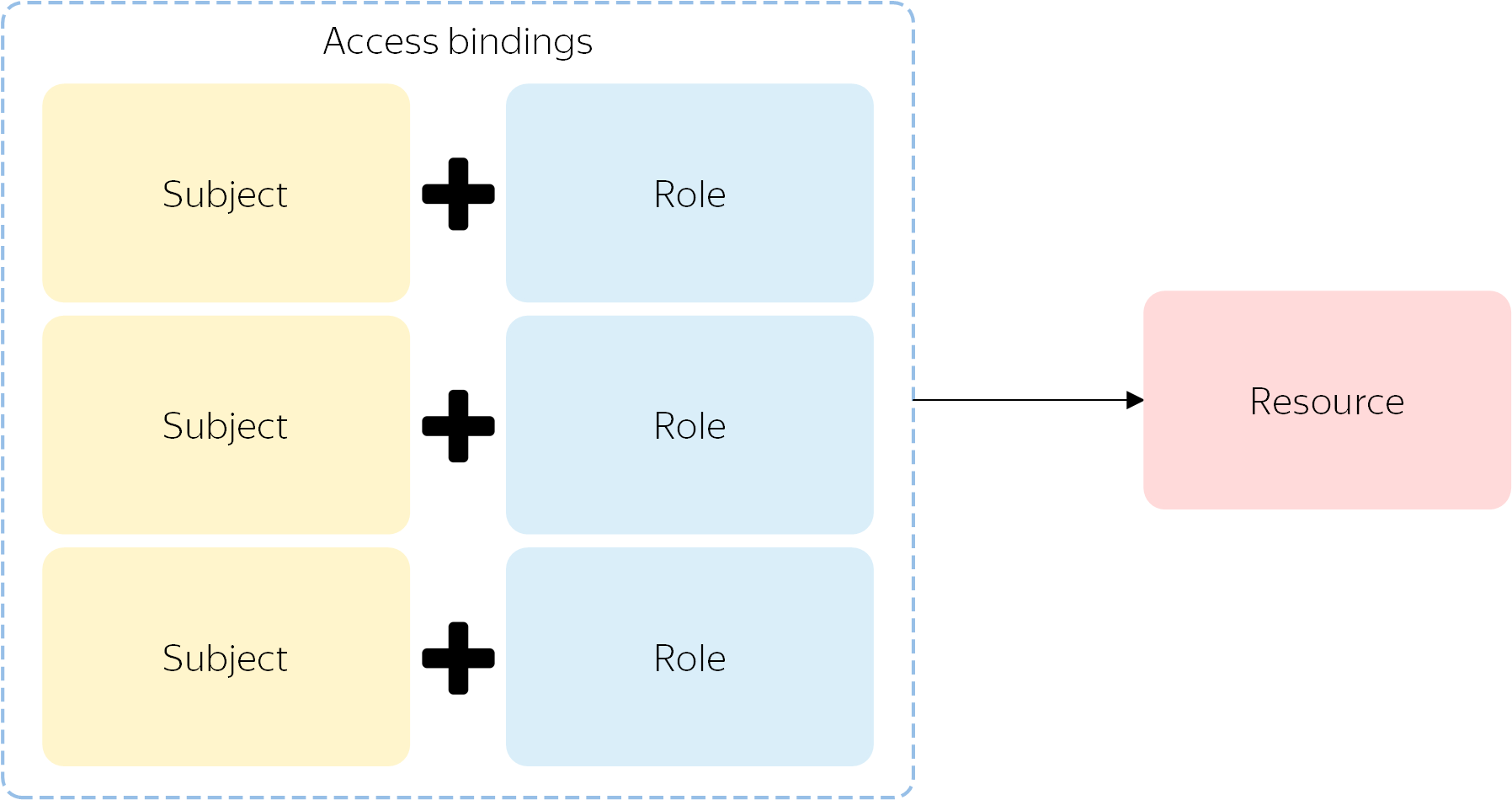
Each binding is a single assignment of a role to a subject. To assign a user multiple roles for a resource, set a separate binding for each role.
Inheriting access permissions
If a resource has child resources, all permissions from the parent resource will be inherited by the child resources. For example, if you assign the user a role for a folder containing a VM, all the role's permissions will also apply to the VM.
If a child resource is also assigned some roles, a list of permissions for this resource will be combined with a list of permissions for its parent resource. You cannot limit the list of permissions inherited from the parent resource.
Access control restrictions in the management console
Some restrictions apply to assigning roles in the management console:
- You cannot assign roles to multiple subjects at once, unlike in the API or CLI. In the management console, you should first select the subject (user or service account) and then assign roles to it.
Managing service access to user cloud resources
Yandex Identity and Access Management allows you to manage service access to resources in a user cloud by enabling or disabling the relevant services.
Service control is the whole of the access permissions needed to create and operate the service's resources in the user's cloud. Such access permissions are assigned to special service accounts, service agents, which the service uses to access the user's resources in the cloud.
The user cannot directly create or delete service agents. All the required service agents with the appropriate access permissions are automatically created when you enable a service and get deleted when you disable it.
See also
For more information about managing access to a specific Yandex Cloud service, see the Access management
section in the documentation for that service.
Step-by-step guides and examples: