Jupyter Notebook has a cell structure, allowing you to run code snippets from any cell in any order

Four core products to train ML professionals
Learn which services and courses the universities and EdTech projects use to train machine learning specialists.
We talked to eight education experts from different schools and universities. There are many platforms for hands-on learning, but none offer a comprehensive solution. That is why teachers mix different tools to find a combination that works best for them.
Maksim Kulayev, Program Director of the Data Analyst course at Skillbox, believes open-source tools play a key role in training future IT professionals. “Each tool requires a different level of background knowledge, but that is what makes it easier for students to level up gradually,” he explained.
ML course authors want students to practice in the same environments they will face in their future jobs. That is what matters when choosing tools. Our interviewees listed around ten platforms they use, four from which were clearly the most popular.
We aim to give students a clear view of what each architecture offers, both its strengths and flaws, without losing out on quality. Since most our tasks run on free or freemium tools having strict time limits, we plan the assignments to make sure everything fits.
1. Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter is still a core tool for data scientists. Its notebook-style interface made it popular, allowing users to work with source code in a flexible way. It runs code snippets without the need to compile or deploy anything on the user-side platform.
This works especially well for ML experts. With Jupyter, they can run experiments quickly and skip unnecessary steps. For example, they can train a model on a small dataset, check the results at once, then change the settings and run a new test, repeating this process until they get the best outcome.
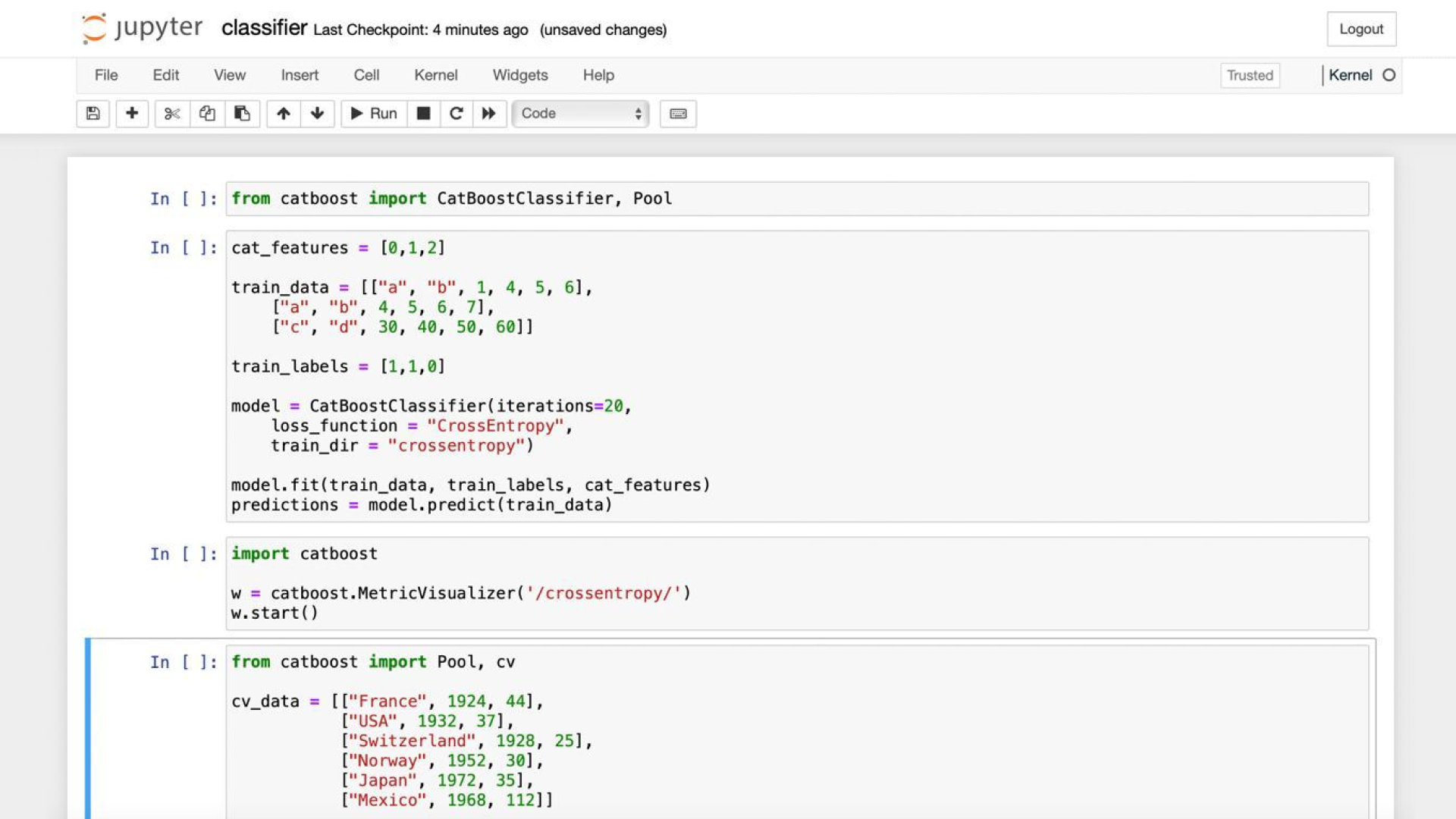
However, such an approach also has its downside.
Jupyter is not always the best fit for large-scale projects, since keeping the code clean and readable can be difficult. Still, it makes the learning process more accessible and easier for students to understand.
Typically, Jupyter runs locally, installed either on lab computers and laptops or students' personal devices.
2. Google Сolab and Kaggle
Google Colab is a cloud-based coding space. Since it supports the latest versions of libraries and environments, it works well for nearly all model training tasks.
The biggest advantage of this tool is that it is free. It also gets praise for offering a pre-built environment that fits most use cases. On the downside, it lacks a local file system (you can use Google Drive instead), and its features are somewhat limited.
Google Workspace is not as powerful as its Microsoft counterpart, but it stands out for being both free and cloud-native.
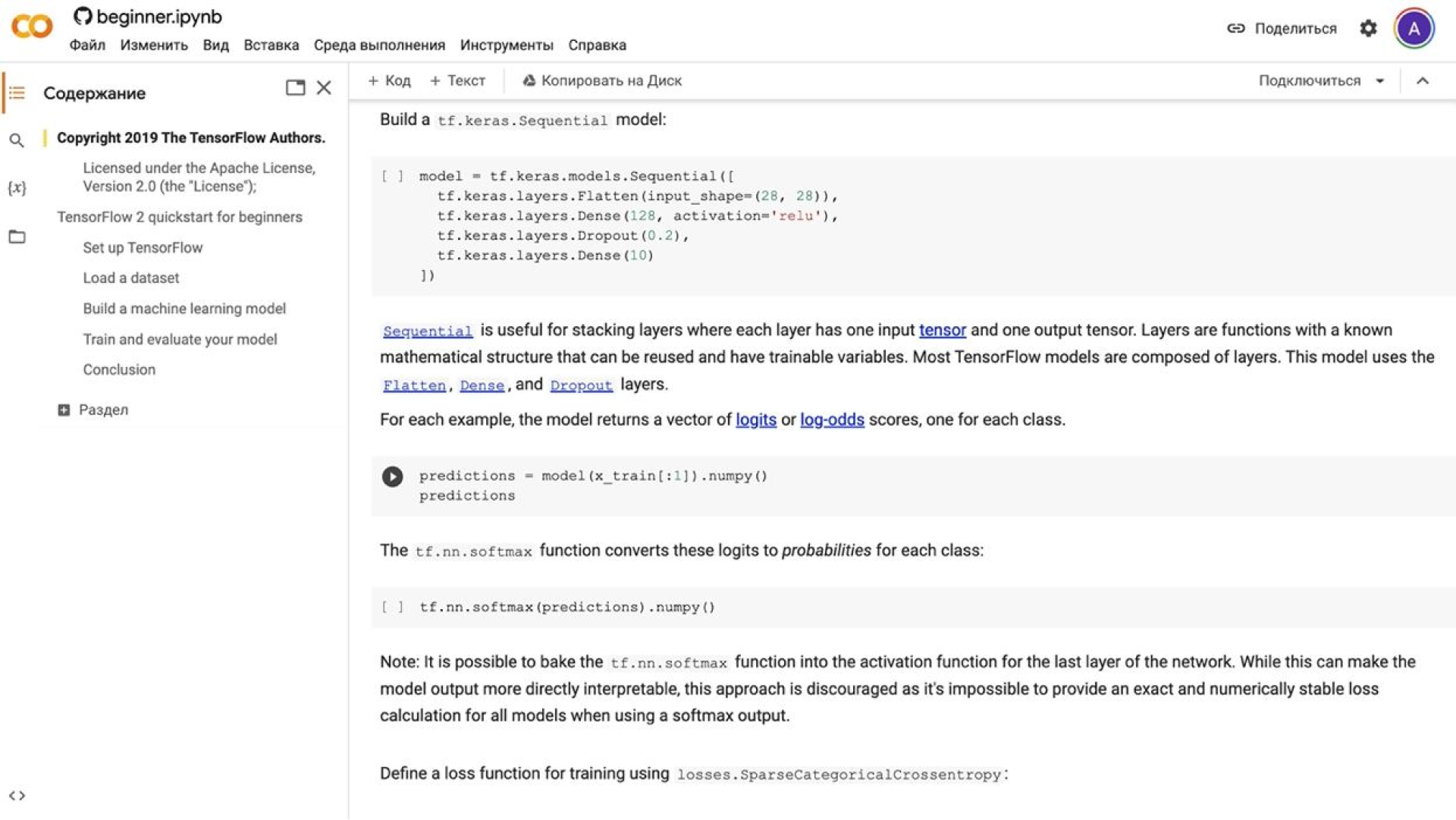
Google Сolab interface
Everything works fine as long as the computations are short. With longer runs, however, there is a real risk that the VM will shut down and you will lose all your progress. Saving to Google Drive helps, but you still need to re-run many steps.
Paired with Colab, Kaggle is another part of the Google’s ecosystem. It is a platform where data scientists compete in contests focused on data analysis. It also serves as a kind of social network for data and machine learning experts.
For example, the Kazan Federal University’s Institute of Information Technology and Intelligent Systems (ITIS) uses Kaggle to review educational course materials. According to the ITIS professors, Kaggle offers strong practices for solving ML project tasks and methods for model interpretation.
For tabular data, Google Colab and Kaggle generally provide enough resources. However, when it comes to neural networks, their computing limits make it difficult to run the experiments we want in class.
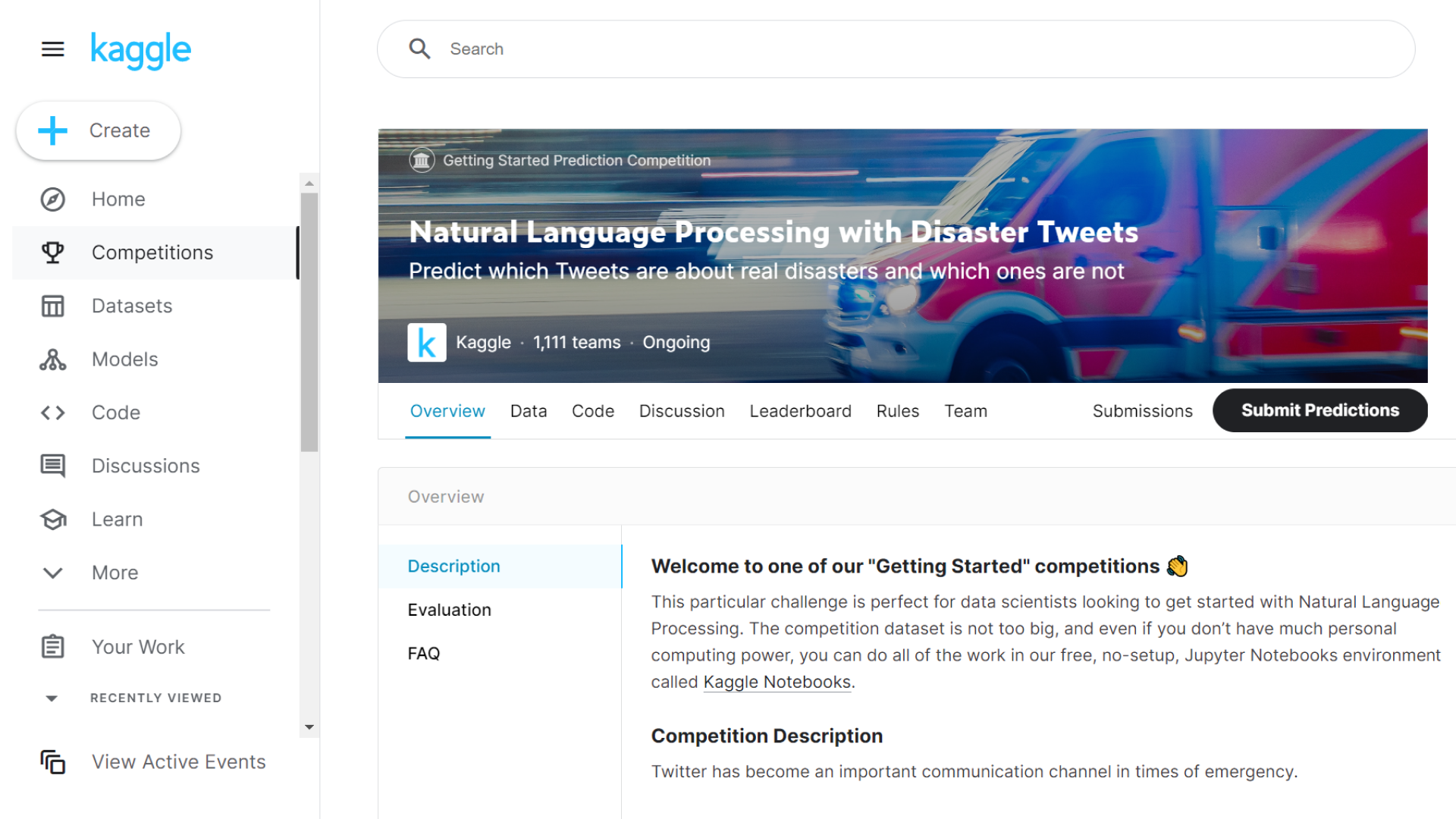
Section with Kaggle competitions involving students from KFU’s ITIS
Other universities mention the same issue.
Google Сolab and Kaggle are popular for their user-friendly interface and solid functions. Their performance cover most educational needs, but strict quotas they impose can be a barrier in the learning process.
3. Dataproc and Apache Spark™
Machine learning tasks often involve large amounts of data, sometimes up to dozens of terabytes. Running that on a single machine may take days.
This is where MapReduce comes in. It splits the data across multiple machines in a cluster, with each one handling its chunk concurrently. That way, the task gets done in just a few hours. Such tools as DataProc and Spark™ make this possible.
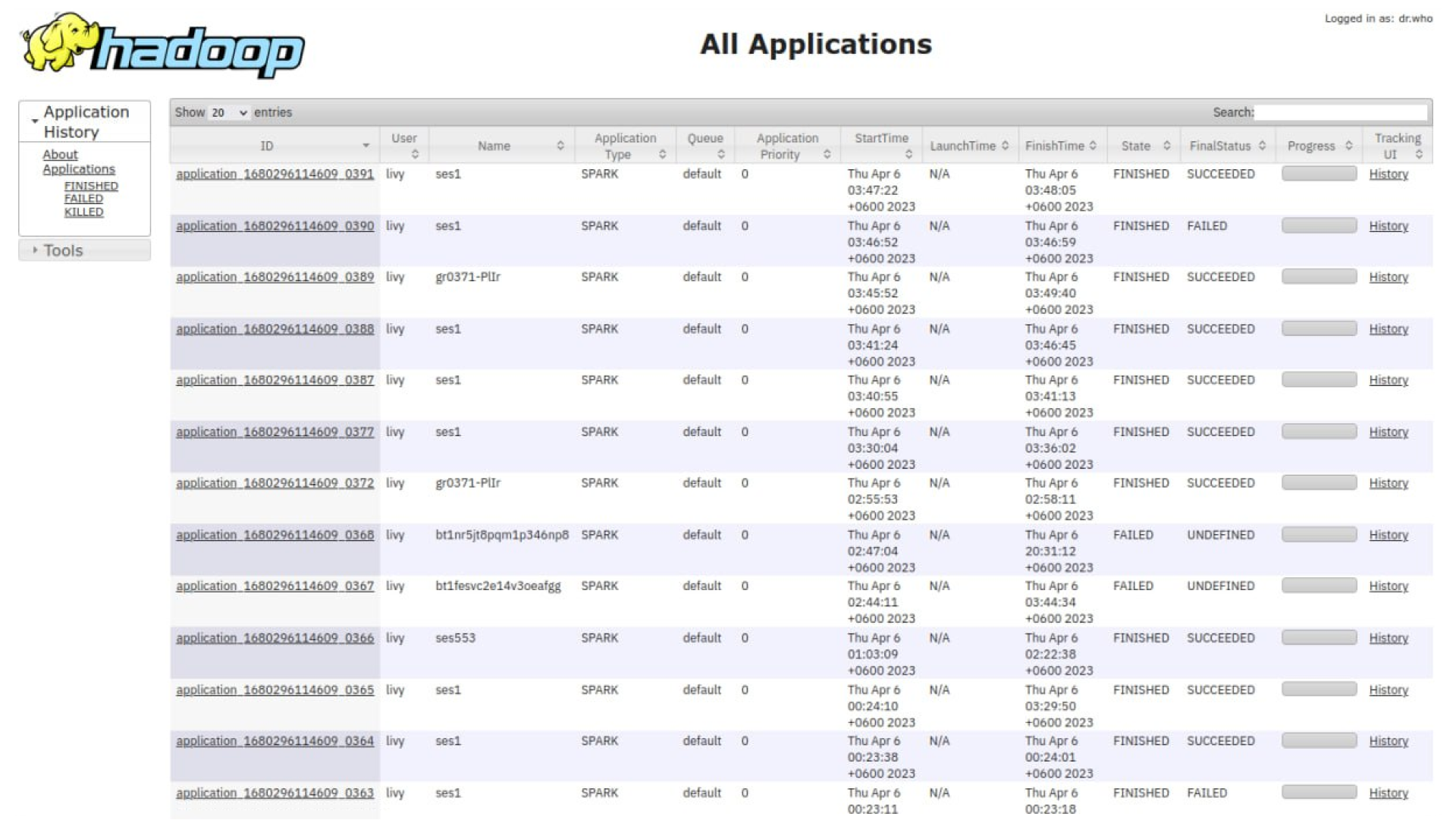
Log of tasks completed by the Saint Petersburg Electrotechnical University students using DataProc
After watching a Yandex Cloud stream about Yandex DataProc, we decided to create a course on big data analysis using Apache Spark™ clusters. The idea was to give our students an opportunity to work with distributed data and computation systems using real-world tools widely used in the industry.
Such tools as Dataproc and Apache Spark™ are quite advanced, while many ML projects often do not need that much data. However, if you want to work at a high level, you should know how to use them.
4. Yandex DataSphere
At Yandex Cloud, we also build our own tools for ML development. One of them is Yandex DataSphere, a serverless platform that keeps hardware utilization close to 100%. This means you only pay for compute time, with no idle resources.
Its integration with other essential ML tools, like Yandex Data Proc, is another reason it stands out.
Yandex DataSphere works well for teams, too. Its flexible entity model allows setting up contexts for both development teams and student groups. Apart from that, you can fine-tune visibility settings, such as assign shared tasks to everyone but keep each student’s project hidden from others.
Anton Naumov from the School of Data Analysis (SDA) pointed out a native file system as a major advantage of Yandex DataSphere. It allows saving both the results and the entire project, meaning you do not have to set up your environment again each time, like you do in Colab.
Still, there are some drawbacks. Anton mentioned that it was sometimes tricky to add all required packages, leading to workarounds. He also noted occasional problems accessing VMs during peak usage. We are already working on speeding up machine allocation and making the environment setup easier.
Uploading a dataset
In Yandex DataSphere, students can create custom Livy sessions and set the compute parameters for the code cells they send. This mattered to us, as students needed to understand how scaling cluster resources affects data analysis during their practice.
Insights from the Yandex Cloud team
Our specialists believe that the combination of these four services is both reasonable and well-balanced.
The ML development market in Russia is split between companies keeping their own hardware stack and using on-premise solutions installed on local computers and those migrating to cloud platforms. Hybrid setups also happen quite often.
In such cases, ML specialists need skills in both cloud and on-premise environments. That is why it is important to give students the chance to master both. The tools mentioned above and their equivalents provide just that kind of hands-on training.
Nikita Volkov, representing both The Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT) and SDA, shared that their university considered using Yandex DataSphere to provide students with GPU access, but it was too costly. That concern came up across other universities, too, so we worked out a solution.
Two years ago, Yandex Cloud launched a grant initiative to support academic courses and research projects in computer science. Since then, we have backed over 100 universities and research centers and introduced their scientists, professors, and students to our cloud tools.
When we start working with a university, we run intro sessions and webinars, and share useful scripts and cases. Some of our services come with ready-made learning content which is already in use at more than 50 universities.
We also offer grants to test our cloud services, although the applicants must meet certain conditions. For example, we recently launched a new program that gives educational institutions free access to Yandex DataSphere.









