Creating a WordPress website using Terraform
To create and set up a WordPress website using Terraform:
If you no longer need the resources you created, delete them.
Get your cloud ready
Sign up in Yandex Cloud and create a billing account:
- Navigate to the management console
- On the Yandex Cloud Billing
ACTIVEorTRIAL_ACTIVEstatus. If you do not have a billing account, create one and link a cloud to it.
If you have an active billing account, you can navigate to the cloud page
Learn more about clouds and folders.
Make sure the selected folder has a cloud network with a subnet in at least one availability zone. To do this, select VPC on the folder page. If the list contains a network, click its name to see the list of subnets. If the subnets or network you need are not listed, create them.
Required paid resources
The cost of maintaining a WordPress website includes:
- Fee for a continuously running VM (see Yandex Compute Cloud pricing).
- Fee for using a dynamic or static public IP address (see Yandex Virtual Private Cloud pricing).
- Fee for public DNS queries and DNS zones if using Yandex Cloud DNS (see Cloud DNS pricing).
Create an infrastructure
With Terraform
Terraform is distributed under the Business Source License
For more information about the provider resources, see the documentation on the Terraform
To create an infrastructure using Terraform:
-
Install Terraform, get the authentication credentials, and specify the source for installing the Yandex Cloud provider (see Configure a provider, step 1).
-
Prepare the infrastructure description files.
Ready-made archiveManually- Create a folder for the files.
- Download the archive
- Unpack the archive to the folder. As a result, the
wordpress.tfconfiguration file should appear in it.
-
Create a folder.
-
Create a configuration file named
wordpress.tfin the folder:wordpress.tf
terraform { required_providers { yandex = { source = "yandex-cloud/yandex" version = ">= 0.47.0" } } } provider "yandex" { zone = "ru-central1-a" } resource "yandex_compute_image" "wordpress" { source_family = "wordpress" } resource "yandex_compute_disk" "boot-disk" { name = "bootvmdisk" type = "network-hdd" zone = "ru-central1-a" size = "20" image_id = yandex_compute_image.wordpress.id } resource "yandex_compute_instance" "vm-wordpress" { name = "wordpress" platform_id = "standard-v3" resources { core_fraction = 20 cores = 2 memory = 1 } boot_disk { disk_id = yandex_compute_disk.boot-disk.id } network_interface { subnet_id = yandex_vpc_subnet.subnet-1.id nat = true security_group_ids = ["${yandex_vpc_security_group.sg-1.id}"] } metadata = { ssh-keys = "<username>:<SSH_key_contents>" } } resource "yandex_vpc_security_group" "sg-1" { name = "wordpress" description = "Description for security group" network_id = yandex_vpc_network.network-1.id ingress { protocol = "TCP" description = "ext-http" v4_cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] port = 80 } ingress { protocol = "TCP" description = "ext-https" v4_cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] port = 443 } egress { protocol = "ANY" description = "any" v4_cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } } resource "yandex_vpc_network" "network-1" { name = "network1" } resource "yandex_vpc_subnet" "subnet-1" { name = "subnet1" zone = "ru-central1-a" network_id = yandex_vpc_network.network-1.id v4_cidr_blocks = ["192.168.1.0/24"] } resource "yandex_dns_zone" "zone-1" { name = "example-zone-1" description = "Public zone" zone = "example.com." public = true } resource "yandex_dns_recordset" "rs-1" { zone_id = yandex_dns_zone.zone-1.id name = "example.com." ttl = 600 type = "A" data = ["${yandex_compute_instance.vm-wordpress.network_interface.0.nat_ip_address}"] } resource "yandex_dns_recordset" "rs-2" { zone_id = yandex_dns_zone.zone-1.id name = "www" ttl = 600 type = "CNAME" data = ["example.com"] }
For more information about the properties of Terraform resources, see the relevant Terraform guides:
-
Under
metadata, specify the metadata for creating a VM:<username>:<SSH_key_contents>. Regardless of the username specified, the key is assigned to the user set in the WordPress image configuration. Such users vary depending on an image. For more information, see Keys processed in public images Yandex Cloud. -
Create the resources:
-
In the terminal, change to the folder where you edited the configuration file.
-
Make sure the configuration file is correct using the command:
terraform validateIf the configuration is correct, the following message is returned:
Success! The configuration is valid. -
Run the command:
terraform planThe terminal will display a list of resources with parameters. No changes are made at this step. If the configuration contains errors, Terraform will point them out.
-
Apply the configuration changes:
terraform apply -
Confirm the changes: type
yesin the terminal and press Enter.
-
Configure WordPress
To configure WordPress:
After the wordpress VM's status changes to RUNNING, do the following:
-
Under Network on the VM page in the management console

-
Open the domain name you configured or the VM's address in the browser.
-
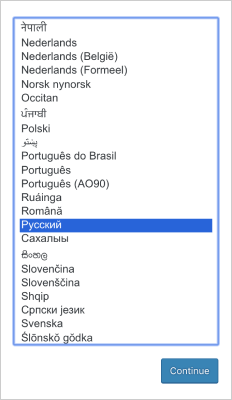
Select the language and click Continue.
-
Fill out information to access the website:
- Enter any name for the website (for example,
yc-wordpress). - Specify the username to be used to log in to the admin panel (for example,
yc-user). - Enter the password to be used to log in to the admin panel.
- Enter your email address.
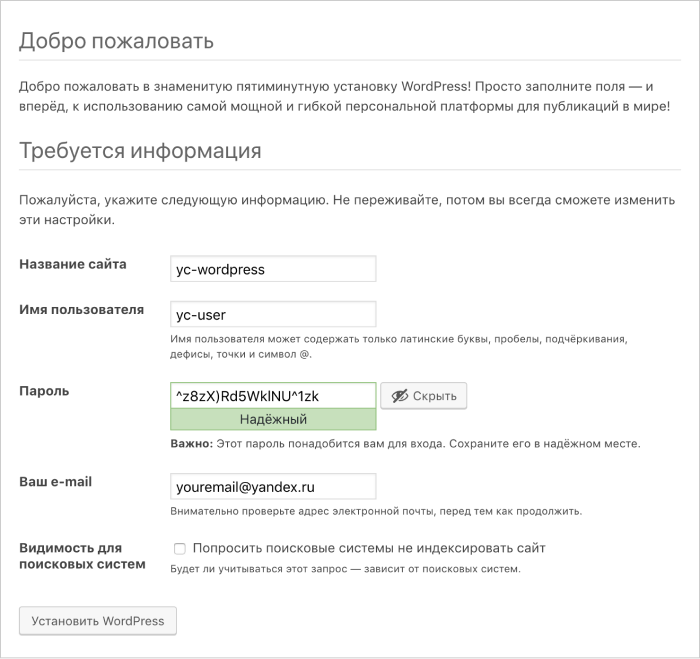
- Enter any name for the website (for example,
-
Click Install WordPress.
-
If the installation is successful, click Log in.
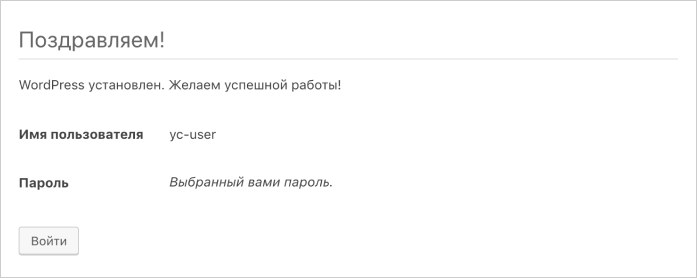
-
Log in to the website with the username and password specified in the previous steps. This will open the admin panel where you can start working with your website.
-
Make sure the website is accessible by opening the VM's public IP address in your browser.
How to delete the resources you created
To stop paying for the resources you created:
-
Open the
wordpress.tfconfiguration file and delete your infrastructure description from it. -
Apply the changes:
-
In the terminal, change to the folder where you edited the configuration file.
-
Make sure the configuration file is correct using the command:
terraform validateIf the configuration is correct, the following message is returned:
Success! The configuration is valid. -
Run the command:
terraform planThe terminal will display a list of resources with parameters. No changes are made at this step. If the configuration contains errors, Terraform will point them out.
-
Apply the configuration changes:
terraform apply -
Confirm the changes: type
yesin the terminal and press Enter.
-