Uploading audit logs to Splunk SIEM
Create a trail to upload management event audit logs of resources in an individual folder to an Yandex Object Storage bucket with encryption enabled. Then configure continuous log delivery to SIEM Splunk.
The solution described in the tutorial follows the steps below:
- A trail uploads logs to an Object Storage bucket.
- The bucket is mounted as part of an intermediate VM's filesystem
- The intermediate VM runs a script that pulls logs from the bucket on a schedule and pushes them to Splunk.
To configure delivery of audit log files from a bucket to Splunk:
- Get your cloud ready.
- Set up your environment.
- Assign roles to the service account.
- Create a trail.
- Set up Splunk for import.
- Enable egress NAT for the subnet with the intermediate VM.
- Create an intermediate VM.
- Visualize data in Splunk.
Some steps are completed in Terraform.
If you no longer need the resources you created, delete them.
Getting started
If you do not have the Yandex Cloud CLI installed yet, install and initialize it.
By default, the CLI uses the folder specified when creating the profile. To change the default folder, use the yc config set folder-id <folder_ID> command. You can also set a different folder for any specific command using the --folder-name or --folder-id parameter.
Sign up for Yandex Cloud and create a billing account:
- Navigate to the management console
- On the Yandex Cloud Billing
ACTIVEorTRIAL_ACTIVEstatus. If you do not have a billing account, create one and link a cloud to it.
If you have an active billing account, you can navigate to the cloud page
Learn more about clouds and folders here.
To complete the tutorial, a Splunk instance must be available to the intermediate VM on port 8080.
Required paid resources
The infrastructure support cost includes:
- Fee for using VM instances (see Compute Cloud pricing).
- Fee for storing data in a bucket (see Object Storage pricing).
- Fee for operations with data (see Object Storage pricing).
- Fee for using KMS keys (see Key Management Service pricing).
Set up your environment
Create a new bucket to use for uploading audit logs
- In the management console
- Select Object Storage.
- Click Create bucket.
- On the bucket creation page:
-
Enter a name for the bucket consistent with the naming requirements.
By default, a bucket with a dot in the name is only available over HTTP. To provide HTTPS support for your bucket, upload your own security certificate to Object Storage.
-
Limit the maximum bucket size, if required.
If the value is
0, the size is not limited. It is similar to the enabled No limit option. -
In the Read objects, Read object list, and Read settings fields, select
With authorization. -
Select the default storage class.
-
Click Create bucket to complete the operation.
-
Create an encryption key in Key Management Service
-
In the management console
-
Select Key Management Service.
-
Click Create key and set the key attributes:
- Any name and optional description.
- Encryption algorithm, e.g., AES-256.
- Rotation period (how often to change key versions).
- Click Create.
When creating a key, you create its first version; to open a page with its attributes, click the key in the list.
Enable bucket encryption
-
In the management console
-
In the left-hand panel, select Security.
-
Open the Encryption tab.
-
In the KMS Key field, select an existing key or create a new one:
- If the folder does not contain any keys yet, click Create key. If the folder contains keys but they are not suitable, click Create.
- Enter a name for the key.
- Select an encryption algorithm and a rotation period.
- Click Create.
-
Click Save.
Create a service account
-
In the management console
-
In the list of services, select Identity and Access Management.
-
Click Create service account.
-
Enter a name for the service account. Follow these naming requirements:
- Length: between 3 and 63 characters.
- It can only contain lowercase Latin letters, numbers, and hyphens.
- It must start with a letter and cannot end with a hyphen.
-
Click Create.
Assign roles to the service account
-
Assign the audit-trails.viewer role to the folder whose resources will be polled for audit logs:
yc resource-manager folder add-access-binding \ --role audit-trails.viewer \ --id <folder_ID> \ --service-account-id <service_account_ID>Where:
--role: Role being assigned.--id: ID of the folder from which audit logs will be collected.--service-account-id: Service account ID.
-
Assign the storage.uploader role to the folder to host the trail:
yc resource-manager folder add-access-binding \ --role storage.uploader \ --id <folder_ID> \ --service-account-id <service_account_ID>Where:
--role: Role you want to assign.--id: ID of the folder to host the trail.--service-account-id: Service account ID.
-
Assign the kms.keys.encrypterDecrypter role to the encryption key:
yc kms symmetric-key add-access-binding \ --role kms.keys.encrypterDecrypter \ --id <KMS_key_ID> \ --service-account-id <service_account_ID>Where:
--role: Role being assigned.--id: KMS key ID.--service-account-id: Service account ID.
Create a trail
To create the trail, make sure you have the following roles:
iam.serviceAccounts.userfor the service account.audit-trails.editorfor the folder to host the trail.audit-trails.viewerfor the folder from which audit logs will be collected.storage.viewerfor the bucket or folder.
-
In the management console
-
Select Audit Trails.
-
Click Create trail and specify:
- Name: Name of the new trail.
- Description: Trail description (optional).
-
Under Destination, configure the destination object:
- Destination:
Object Storage. - Bucket: Name of the bucket to which you want to upload audit logs.
- Object prefix: Optional parameter used in the full name of the audit log file.
Note
Use a prefix to store audit logs and third-party data in the same bucket. Do not use the same prefix for logs and other bucket objects because that may cause logs and third-party objects to overwrite each other.
- Encryption key: Specify the encryption key the bucket is encrypted with.
- Destination:
-
Under Service account, select the service account that the trail will use to upload audit log files to the bucket.
-
Under Collecting management events, configure the collection of management event audit logs:
- Collecting events: Select
Enabled. - Resource: Select
Folder. - Folder: Automatically populated field containing the name of the current folder.
- Collecting events: Select
-
Under Collecting data events, select
Disabledin the Collecting events field. -
Click Create.
Warning
The solution will delete the logs from the bucket after they are exported to Splunk. If you need to keep the logs in the bucket, create a separate bucket and trail.
Set up Splunk for import
Enable HTTPEventCollector and follow this guideEvent Collector token.
Set up a NAT gateway for the subnet with the intermediate VM
- Create a NAT gateway:
-
In the management console
-
In the list of services, select Virtual Private Cloud.
-
In the left-hand panel, select Gateways.
-
Click Create.
-
Enter a name for the gateway. Follow these naming requirements:
- Length: between 3 and 63 characters.
- It can only contain lowercase Latin letters, numbers, and hyphens.
- It must start with a letter and cannot end with a hyphen.
-
The default gateway type is
Egress NAT. -
Click Save.
-
- Create a route table:
- In the left-hand panel, select
- Click Create to add a new table, or select an existing one.
- Click Add.
- In the window that opens, select
Gatewayin the Next hop field. - In the Gateway field, select the NAT gateway you created. The destination prefix will apply automatically.
- Click Add.
- Click Save.
- In the left-hand panel, select
- Link the route table to the subnet where you want to deploy the intermediate VM, to forward its traffic via the NAT gateway:
- In the left-hand panel, select
- In the row with the subnet, click
- In the menu that opens, select Link routing table.
- In the window that opens, select the table you created from the list.
- Click Link.
- In the left-hand panel, select
Create a VM for continuous log delivery to Splunk
-
If you do not have Terraform yet, install it and configure the Yandex Cloud provider.
-
Clone a repository
git clone https://github.com/yandex-cloud-examples/yc-export-auditlogs-to-splunk.git -
Create a subfolder in
/yc-export-auditlogs-to-splunk/terraform/and go there. -
Create a configuration file to invoke the
yc-splunk-trailmodule:module "yc-splunk-trail" { source = "../modules/yc-splunk-trail/" folder_id = <folder_ID> splunk_token = <Event_Collector_token> splunk_server = <your_Splunk_server_address>:8088 bucket_name = <bucket_name> bucket_folder = <name_of_root_folder_in_bucket> sa_id = <service_account_ID> coi_subnet_id = <subnet_ID> }Where:
folder_id: Folder ID.splunk_token: Event Collector token retrieved from Splunk.splunk_server: Address of your Splunk server ashttps://<host_name_or_address>.bucket_name: Bucket name.bucket_folder: Name of the root folder in the bucket.sa_id: Service account ID.coi_subnet_id: ID of the subnet where you set up the NAT gateway.
-
Make sure the configuration files are correct:
terraform planIf the configuration description is correct, the terminal will display a list of the resources being created and their settings. If the configuration contains any errors, Terraform will point them out.
-
Deploy the cloud resources.
-
If the configuration does not contain any errors, run this command:
terraform apply -
Confirm resource creation: enter
yesin the terminal and press Enter.
-
Visualize data in Splunk
-
Go to Splunk and search for the events created by the service account:
index="main" authentication.subject_type="SERVICE_ACCOUNT" | stats count by event_type -
To visualize the results, go to the Visualization tab and select a suitable format (
LineChart,PieChart, etc.):Data visualization example:
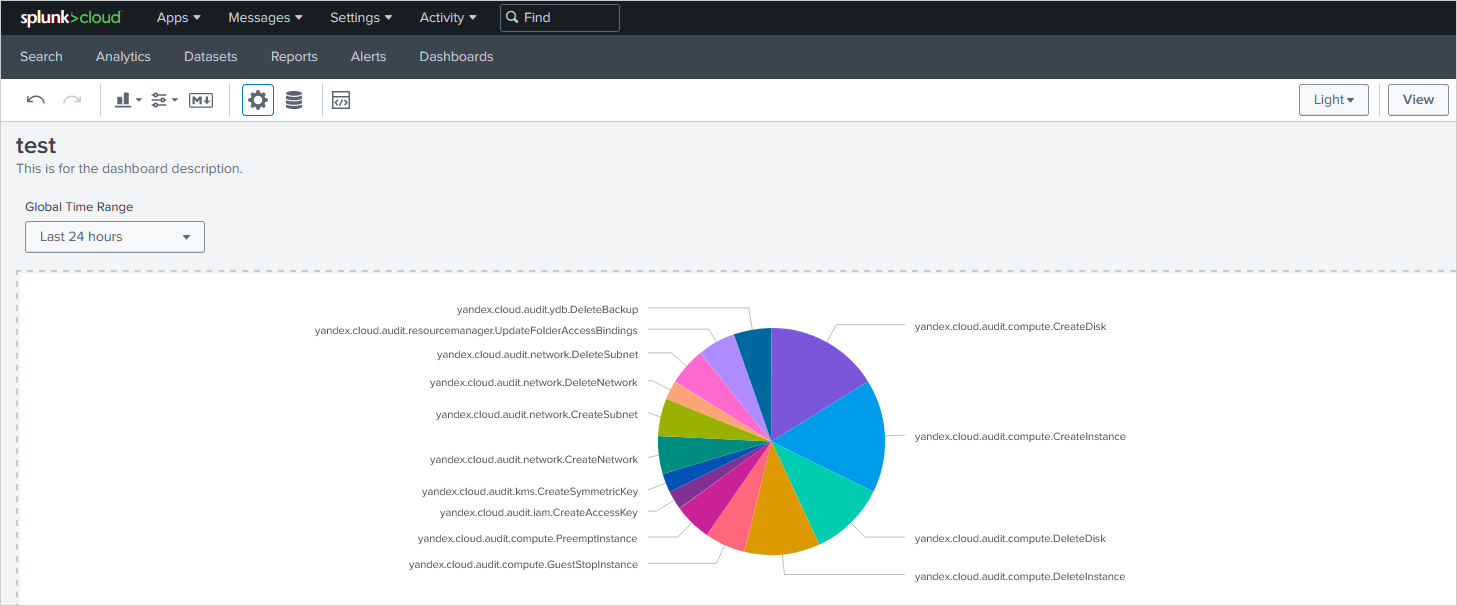
How to delete the resources you created
Some resources are not free of charge. To avoid unnecessary charges, delete the resources you no longer need:
-
To delete the resources created with Terraform:
-
Run this command:
terraform destroyWarning
Terraform will delete all the resources that you created in the current configuration, such as networks, subnets, virtual machines, and so on.
After the command is executed, the terminal will display a list of resources to be deleted.
-
To confirm deletion, type
yesand press Enter.
-